How to Fill Out a 1040 Form?
One of the most important official U.S. tax documents is the 1040 tax form, through which taxpayers report their income. It has several variations, but this one is the main one for most people. From this article, you will learn about the features of filling out and submitting this paper to the IRS.
What Is a 1040 Form?
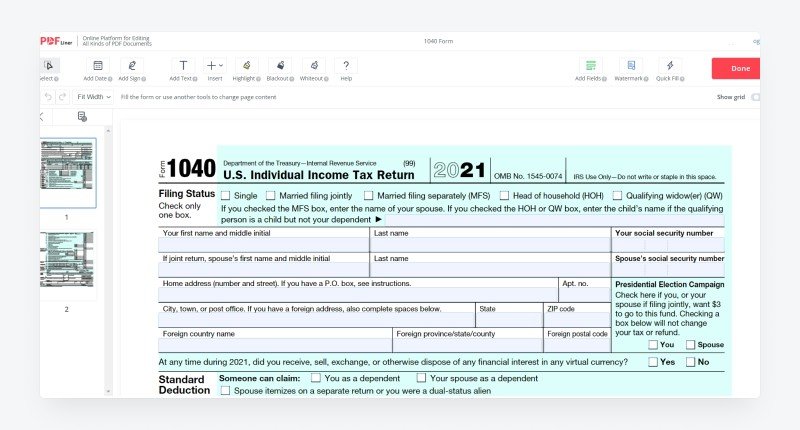
Form 1040 is also called Individual Income Tax Return issued by the Internal Revenue Service. This file consists of only two lists and contains lines for income of any kind. It has handy fields where you need to enter the specified data and add or subtract them depending on the comments to get the amount you should pay. Fillable 1040 Form was last revised in 2021 and has not been significantly changed from the 2020 version. This document has several Schedules that you may need depending on your financial situation and activities. We will talk about them below.
Who Should File a 1040 Tax Form?
In short, every US citizen whose income exceeds $400 should complete a fillable 1040 Form annually. More specific information from the IRS includes a fairly extensive list of who should complete this paper. For example, the tax office requires you to file a tax return if you receive income from a partnership, S corporation, trust, insurance policy dividends, taxable interests, and so on. You may also need to fill out this form if your employer has not deducted Medicare and Social Security taxes from your paycheck, you received some payments from a foreign trust, you intend to get a premium tax credit, you need to pay AMT, and much more.
How to Fill Out a 1040 Form?
As already mentioned, the document is a two-page file, so filling it out will not take you much time. Please note that you may need additional documents to complete some fields, such as Form 1099 and W-2.
- You should pick your filing status and provide information about yourself and your spouse (if any): full name, SNN, and residential address. If you have dependents, list them all.
- After specifying personal information, proceed to the calculation of total income. To do it, you need to list all the ways in which funds were received in the past tax year (tips, salaries, wages, pensions, and other benefits) and add them up.
- Subtract adjustments, if any, to get adjusted gross income. Then add itemized or standard deductions to find the amount you should pay tax.
- Next, go to the total tax calculation and follow the Form 1040 instructions. Consider information from supplemental Schedules, recovery rebate or child tax credit, and so on. When you receive the final amount, calculate the refund you want to get.
- After deducting the refund amount from the total tax, you will receive the amount you should pay for the past tax year.
Be sure to double-check that your calculations are correct, make sure there are no typos, and sign at the end of the document.
What Are the Different Schedules Used With Form 1040?
The IRS also issues several Form 1040 schedules, which cover almost all areas of activity:
- Schedule 1 to declare additional sources of income (for example, alimony and unemployment benefits);
- Schedule 2 to inform the IRS of other taxes due such as household or self-employment ones;
- Schedule 3 is used to declare other credits that are not included in the main document;
- Schedule A to list all itemized deductions (e.g., medical expenses or mortgage interests);
- Schedule B for declaring financial receipts from interests and dividends above $1500;
- Schedule C is used if you have business losses or income (needed by freelancers and independent contractors);
- Schedule D to inform about income and losses from your investments;
- Schedule E is needed if you have financial gains or losses from partnerships, estates, royalties, etc.;
- Schedule F is used by those who have income from agriculture;
- Schedule H should be completed by taxpayers who work as household workers;
- Schedule J is needed by farmers and fishers to declare income from their activities;
- Schedule R is used to obtain a disability or senior credit;
- Schedule SE should be completed by self-employed and business owners whose annual income exceeded $400;
- 8812 is used if you need an additional tax credit for your kids.
Form 1040 and Schedules issued with it provide ample opportunities for declaring any income. Carefully study the features of filling out both the main document and its annexes to submit the necessary information to the tax service on time.
Based on article by pdfliner.com
Read Also: How Project Management Software Can Benefit Your Business